Basel III, the third edition of the Basel Accord, sets international standards for banks’ capital adequacy and stress testing. Basel II was focused more on the capital structures, but Basel III includes more regulations. These regulations are applicable to all banks, big and small. Ask your bank CEO for any questions regarding Basel III. You will find the CEO of your bank more than willing to help.
Contingent forms
Contingent forms of capital (CFSs) are a way for troubled institutions to raise capital through debt securities that convert to equity at prearranged terms. These instruments can reduce the ratio of debt to equity and can be used to recapitalize institutions, without triggering insolvency proceedings.
Banks can use CFSs to comply with Basel III requirements. Under these rules, banks must maintain a minimum capital-to-assets ratio. They must also have sufficient Tier 1 capital to deal with extreme events and reduce the impact of bad loans.

Leverage ratio
The Basel III framework's most important measure for banks is the leverage ratio. It is calculated by dividing a bank's supervisory Tier 1 capital by its total exposure. A low leverage ratio means that the bank is not under capital stress, while a high ratio means that the bank is under stress. The relevant accounting standards must be followed when valuing balance sheet items in order to determine the ratio.
Public disclosure is required for leverage ratios. The regulations require banks to disclose their leverage ratios at least quarterly. From June 2021, the leverage ratio will become a minimum requirement for G-SIBs.
Transition periods
Basel III consists of a new set of requirements that will be applicable to all banks around the world. The agreement imposes certain requirements on all banks and establishes transitional times for their implementation. The new requirements will have minimal impact on existing businesses during the transition periods. But, when they are fully implemented, the new rules will likely have a significant impact. We'll be looking at Canada's specific requirements in this article.
Basel III will require banks that they meet certain minimum capital ratios. Each of these minimum capital requirements will require banks hold certain amounts of common equity and Tier-1 capital. New rules will require banks to keep more of their earnings as capital. By requiring banks to have higher capital levels during good times, the goal is to improve the safety of the banking sector.
Phase-ins
During the implementation of Basel III, there will be many issues. One of these is how phase-ins/outs are implemented. Basel Committee states that the economic effects of these changes will be minimal and that the greater systemic stability and safety benefits will outweigh any costs.
The risk-management indicator's sensitivity will be a significant issue. Basel III's new indicator will be more sensitive than the proxy indicator to operational risks. The new indicator will require banks with ten years of quality operational loss data to calculate risk sensitivity. The new measure will not impact small banks but only large banks.
FAQ
Why is it so hard to make smart business decisions?
Complex systems and many moving parts make up businesses. The people who run them must juggle multiple priorities at once while also dealing with uncertainty and complexity.
Understanding the impact of these factors on the system is crucial to making sound decisions.
This requires you to think about the purpose and function of each component. Then, you need to think about how these pieces interact with one another.
It is also worth asking yourself if you have any unspoken assumptions about how you have been doing things. If you don't have any, it may be time to revisit them.
Asking for assistance from someone else is a good idea if you are still having trouble. They might see things differently than you and may have some insights that could help find a solution.
What's the difference between a program and a project?
A project is temporary while a programme is permanent.
Projects usually have a goal and a deadline.
This is often done by a group of people who report to one another.
A program usually has a set of goals and objectives.
It is typically done by one person.
How can we create a culture of success in our company?
A culture of respect and value within a company is key to a productive culture.
It is based on three principles:
-
Everyone has something to contribute
-
People are treated fairly
-
It is possible to have mutual respect between groups and individuals
These values are reflected in the way people behave. They will show consideration and courtesy to others.
They will be respectful of the opinions of other people.
They encourage others to express their feelings and ideas.
Additionally, the company culture encourages open communication as well as collaboration.
People can freely express their opinions without fear or reprisal.
They know mistakes will be accepted as long as they are dealt with honestly.
Finally, the company culture promotes integrity and honesty.
Everyone is aware that truth must be told.
Everyone is aware that rules and regulations apply to them.
No one is entitled to any special treatment or favors.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma uses statistical analyses to locate problems, measure them, analyze root cause, fix problems and learn from the experience.
First, identify the problem.
The data is then analyzed and collected to identify trends.
Next, corrective steps are taken to fix the problem.
The data are then reanalyzed to see if the problem is solved.
This continues until the problem has been solved.
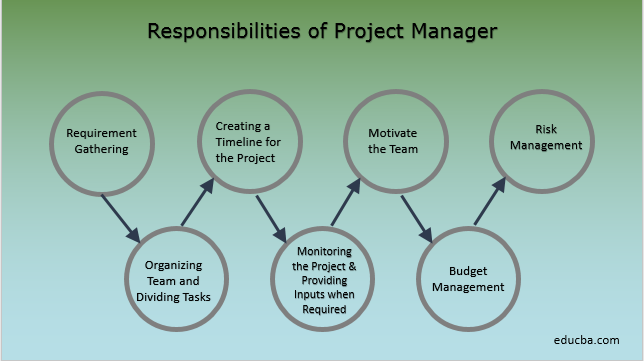
How to manage employees effectively?
Effectively managing employees means making sure they are productive and happy.
It is important to set clear expectations about their behavior and keep track of their performance.
Managers need clear goals to be able to accomplish this.
They need to communicate clearly and openly with staff members. They need to communicate clearly with their staff.
They must also keep track of the activities of their team. These include:
-
What was the result?
-
How much work were you able to accomplish?
-
Who did it?
-
Was it done?
-
Why was this done?
This information can help you monitor your performance and to evaluate your results.
Statistics
- Our program is 100% engineered for your success. (online.uc.edu)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- The profession is expected to grow 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average. (wgu.edu)
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How can you create a Quality Management Plan, (QMP)?
QMP, which was introduced by ISO 9001:2008, is a systematic approach to improving products, services, and processes through continuous improvement. It focuses on the ability to measure, analyze and control processes and customer satisfaction.
QMP is a method that ensures good business performance. The QMP aims to improve the process of production, service delivery, and customer relationship. QMPs should encompass all three components - Products and Services, as well as Processes. When the QMP includes only one aspect, it is called a "Process" QMP. QMP stands for Product/Service. QMP is also used to refer to QMPs that focus on customer relations.
There are two key elements to implementing a QMP: Strategy and Scope. They can be described as follows:
Scope is what the QMP covers and how long it will last. For example, if your organization wants to implement a QMP for six months, this scope will define the activities performed during the first six months.
Strategy: This describes how you will achieve the goals in your scope.
A typical QMP comprises five phases: Planning and Design, Development, Construction, Implementation, Maintenance. Here are the details for each phase.
Planning: This stage is where the QMP objectives are identified and prioritized. In order to fully understand and meet the needs of all stakeholders involved in this project, they are consulted. After identifying the objectives, priorities, and stakeholder involvement, the next step is to develop the strategy for achieving these objectives.
Design: This stage involves the creation of the vision, mission, strategies and tactics necessary to implement the QMP successfully. These strategies are implemented by the development of detailed plans and procedures.
Development: The development team is responsible for building the resources and capabilities necessary to implement the QMP effectively.
Implementation: This is the actual implementation and use of the QMP's planned strategies.
Maintenance: It is an ongoing process that maintains the QMP over time.
Several additional items should be added to the QMP.
Stakeholder involvement is important for the QMP's success. They should be involved in planning, design, development and implementation of the QMP.
Project Initiation: The initiation of any project requires a clear understanding of the problem statement and the solution. Also, the initiator should understand why they are doing it and what they expect.
Time frame: The QMP's timeframe is critical. If you plan to implement the QMP for a short period, you can start with a simple version. However, if you have a long-term commitment, you may require more elaborate versions.
Cost Estimation. Cost estimation is another crucial component of QMP. Without knowing how much you will spend, planning is impossible. Cost estimation is crucial before you begin the QMP.
QMPs are more than just documents. They can also be updated as needed. It can change as the company grows or changes. It should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it meets current needs.